The bones of the fingers and toes are called phalanx (phalanges) after the Ancient Greek army formation. The rows of soldiers are like the arrangement of the digits. The word phalanx originates from the Greek word for log. Now you know!
Phrygian cap: common anatomical variant in gallbladder, caused by folding of fundus, no clinical significance. Named for caps worn by people of Phrygia (Turkey) 1200-700 BCE. Became a symbol of liberty. Also seen on Smurfs.
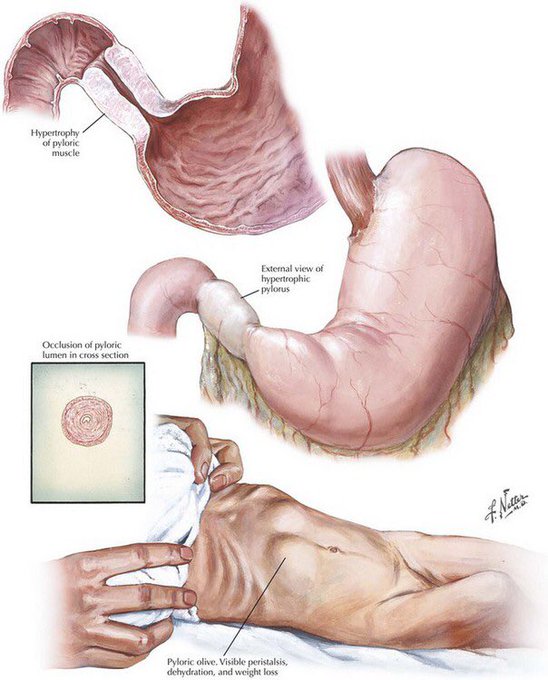
2 cases of congenital hypertrophic pyloric stenosis were described by Danish doctor Harald Hirschsprung in 1888, defining the disease, but reports date back to the 1700s. Pyloromyotomy was reported by German surgeon Conrad Ramstedt in 1912, which dramatically increased survival.
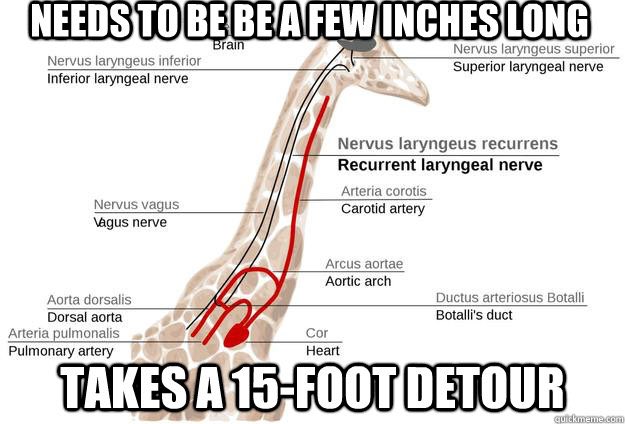
The anatomy and function of the recurrent laryngeal nerve was described by Galen in 2nd century CE, which he demonstrated by cutting it in a squealing pig, rendering it silent. Avoiding this structure is crucial in thyroid surgery. Fun fact: a giraffe’s nerve is 15 feet long!
The Sugarbaker procedure (after Dr. Paul Sugarbaker) for intra-abdominal malignancies, involves complete surgical tumour removal (cytoreduction), including stripping of the peritoneum, intra-operative heated chemo, then post-op intraperitoneal chemo. Takes about 10 hours!
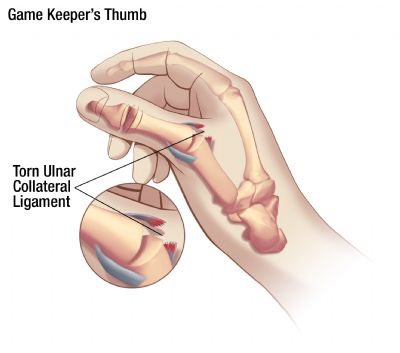
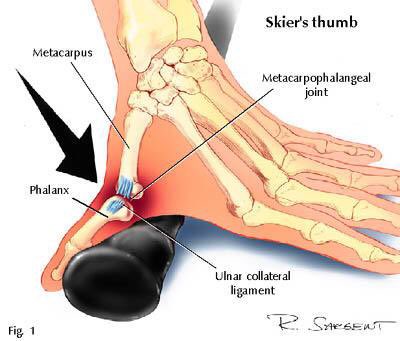
Gameskeeper’s thumb - injury to ulnar collateral ligament. First described in 1955 by CS Campbell, who saw it in Scottish rabbit keepers, who would break the animals’ necks between their thumb and forefinger and the ground. Now more commonly seen in skiers (landing on ski pole).
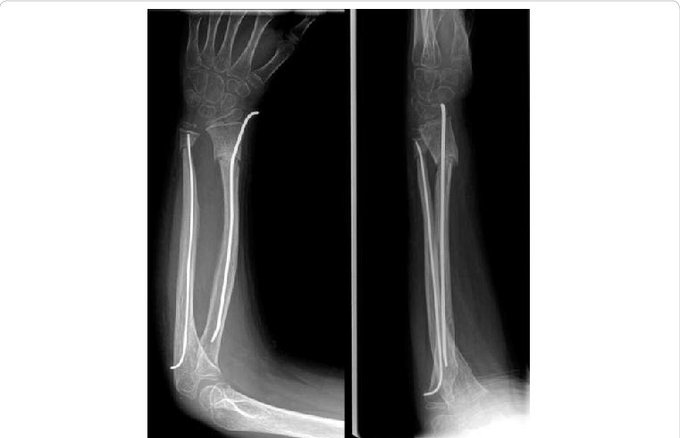
The Nancy Nail, an elastic stable intramedullary nail used in paediatric fractures, was described in the early 1980s by JP Metaizeau at the Children’s Hospital in Nancy, France (hence the name). Thanks @NaanDerthaal for your tweet that made me aware of this nail!
English surgeon John Abernethy (1764-1831) believed most diseases were due to digestion disorders, and so invented a digestive biscuit, similar to hardtack, still popular today! He also described congenital absence of the portal vein in 1793 (Abernethy malformation).
One for the urologists: the verumontanum is a structure in the prostatic urethra. The name comes from Latin and means ‘mountain ridge’. The other name for it, seminal colliculus, also has a Latin root, as colliculus means ‘a small elevation or knoll’. I like the first one better
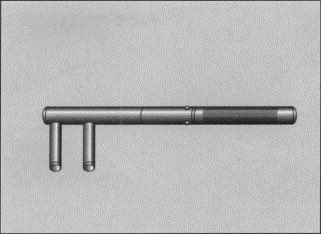
The Thomas wrench was used to forcibly correct clubfoot. It would cause tissue damage and bone fractures. Hugh Owen Thomas (1834-1891), a Welsh surgeon, invented it. Trained as a surgeon, he came from a family of bonesetters. Also known for the Thomas splint and Thomas test.