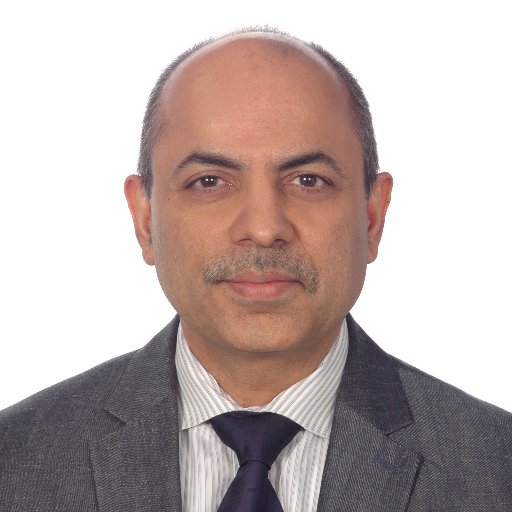
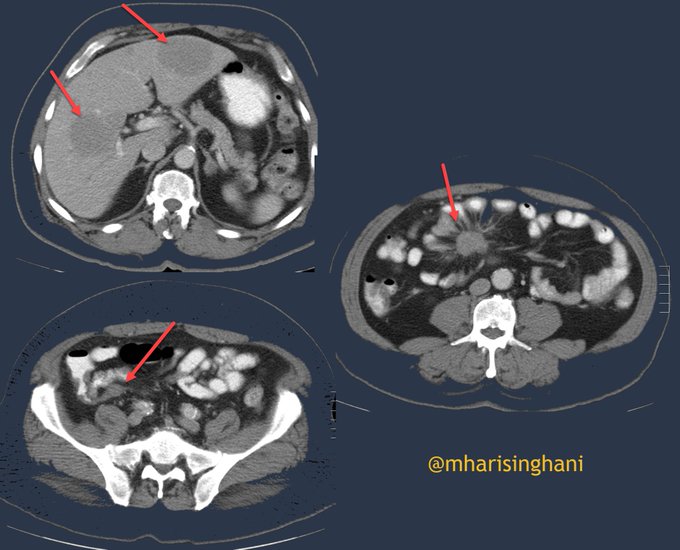
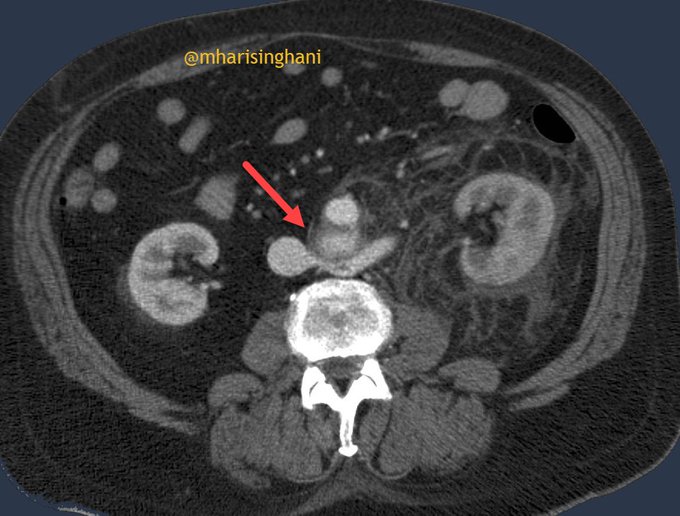
Patient presenting with abdominal pain; spectrum of findings from primary carcinoid tumor arising from appendix, with metastases to mesentery and to liver
Two points to emphasize here; patient with primary prostate cancer; called node in pelvis; request for biopsy; never take non contrast study as final diagnostic study; always make sure you rule out vascular etiology before bx; this was venous varix in pelvis not a node
Peripherally calcified low density (likely cystic) lesion in pancreatic head; neuroendocrine tumor of pancreas
Going through the differential of perinephric soft tissue stranding; primary RP fibrosis; IgG4 disease; lymphoma; Erdheim Chester or the disease that this patient had; Rosai Dorfman disease
A patient presenting with hematuria; rupture of AAA into the renal vein
CT in a patient complaining of abdominal pain; ulcerated GIST nicely seen with positive contrast
Cystic lesion in liver and peritoneum; calcified lesion in liver and in peritoneum; one possibility is metastases but this was hydatid disease
When you find one urothelial lesion; always look hard and close to see if there is another one; as was the case in this patient; tumor in renal pelvis and distal left ureter; TCC
Focal well circumscribed lesion with stellate calcification in an older female patient; occasionally the microcystic nature is tough to discern on CT; hence need MRI; Microcystic serous cystadenoma of pancreas
Bilateral small cysts in the kidneys; patient on long term lithium; lithium toxicity