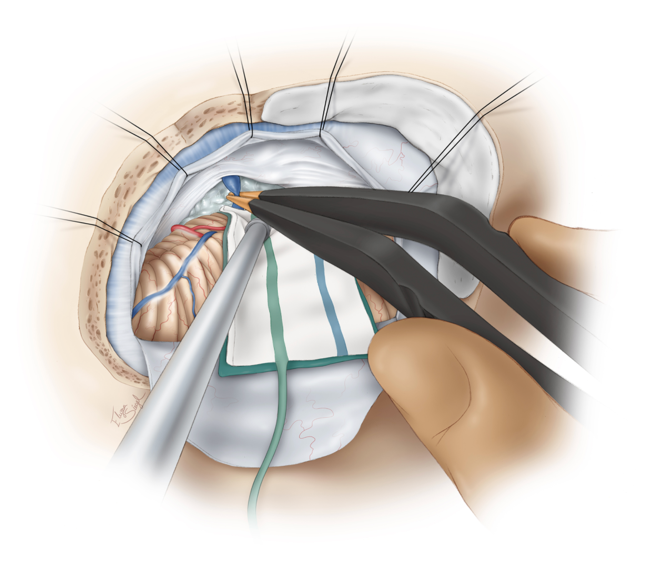
In low-flow revascularization, after craniotomy & identification of a suitable MCA recipient branch, a temporary clip is applied to the proximal STA. The distal end of the STA is cut obliquely (“fish-mouthed”)which allows for increased anastomotic surface. https://t.co/It9CWogvub
The cavernous malformations located in the basal ganglia are readily approached via transcallosal (both ipsi- and contralateral interhemispheric), subfrontal supracarotid, transinsular and transparietal cortical routes.
https://t.co/GXLUz1y5uh
Common operative corridors for access to deep cavernous malformations in periventricular areas are illustrated: https://t.co/GXLUz1y5uh
Seen here are the operative viewing angles (green) and blind spots (red) encountered during a transforaminal transvenous transchoroidal approach, which exposes the third ventricle by enlarging the foramen of Monroe via transection of the septal vein.
https://t.co/Rn1NHc1Ezr
Watch as Dr. Cohen removes an arteriovenous malformation within eloquent cortices using the intranidal resection technique.
The intranidal resection technique allows for maximal protection of vital structures around the nidus.
https://t.co/JZhxEV9GO2
#cerebrovascular #nsgy
During resection for cerebellopontine angle epidermoid cysts, medial mobilization of the petrosal surface of the hemisphere allows exposure of the tumor within the CP angle.
See more here:
https://t.co/k4h4doy0AX
This unique and novel illustration with its layered format provides a road map for surgery within the periclival region. #neurosurgery
See more here:
https://t.co/BfezRCFXqG