nsgyのTwitterイラスト検索結果。 34 件
Here @AaronCohenGadol describes the resection of AVMs within eloquent cortices and more specifically the angular gyrus or language cortex #Nsgy #AVM https://t.co/hNV5m9qJiP
In this operative video, resection of a large acoustic neuroma is demonstrated.
Learn more here:
https://t.co/KXcaWDPiJ6
#nsgy #cranial #tumor
Watch as Dr. Cohen removes an arteriovenous malformation within eloquent cortices using the intranidal resection technique.
The intranidal resection technique allows for maximal protection of vital structures around the nidus.
https://t.co/JZhxEV9GO2
#cerebrovascular #nsgy
In this operative video, Dr. Cohen discusses resection of a craniopharyngioma using an orbitozygomatic craniotomy with a translaminar terminalis approach.
See the pearls here:
https://t.co/vI9bdbZ5sf
#nsgy #tumor #complexcranial
Watch as Dr. Cohen removes an arteriovenous malformation within eloquent cortices using the intranidal resection technique. This technique allows for maximal protection of vital structures around the nidus.
https://t.co/JZhxEV9GO2
#AVMs #cerebrovascular #nsgy
The basic principles of the anterior interhemispheric transcallosal approach are illustrated. The reach of this approach is shaded in green (inset image). #nsgy #neurosurgery #tumor https://t.co/1zAOV1Crte
Patient positioning matters! Here’s a great refresher for incoming #NSGY interns and current residents in this #NeurosurgicalAtlas Ground Rounds: Patient Positioning for Intracranial Surgery with Dr. William Couldwell: https://t.co/lBIDamGpdy @NSTumorSection @cvsection
Deep venous anatomy is key in the management of pineal region tumors. Illustrated here is the location of one such tumor through the occipital transtentorial route. #neurosurgery #brain #tumor #nsgy
https://t.co/QlSSjafpvq
Temporal horn AVMs are technically challenging to tackle because the nidus is covering the feeding vessels emerging from the anterior choroidal artery within the choroidal fissure. #nsgy #neurosurgery #cerebrovascular
Learn more here:
https://t.co/cn2k9dzhwt
The operative view through the more popular transcortical route via the left superior parietal lobule for periatrial lesions is shown with the sagittal suture parallel to the floor. Note the body of the lateral ventricle is inferior here. #nsgy
https://t.co/cn2k9dzhwt
For ventricular body AVMs that extend lateral to the midline, a contralateral transcallosal route is favored to minimize ipsilateral hemispheric retraction. #nsgy #neurosurgery #cerebrovascular
Learn more here:
https://t.co/cn2k9dzhwt
During a transsylvian amygdalohippocampectomy, incising the temporal stem allows for access to the temporal horn and serves to create a corridor through which the amygdala and hippocampus can be removed. #neurosurgery #brain #neuroanatomy #nsgy
https://t.co/q4fP0e4Ukc
The Artery of Adamkiewicz ascends on the mid-sagittal anterior spinal cord and makes a characteristic hairpin turn as it anastomoses with the anterior spinal artery. It richly supplies the thoracolumbar spinal cord. #nsgy #spine #neuroanatomy
https://t.co/tBbewYe6wY
In this video, Dr. Cohen performs removal of a left medial occipital arteriovenous malformation (#AVM).
See more here:
https://t.co/U09pdR7Nbi
#nsgy #cerebrovascular
Continuing on with our theme from last week of #skullbase reconstruction: Abdominal or thigh fat can be buttressed with a bony septum or prosthesis to keep the fat in place and reconstruct the sella floor. #nsgy #neurosurgery #medtwitter
https://t.co/ZSbv8Gt1uM
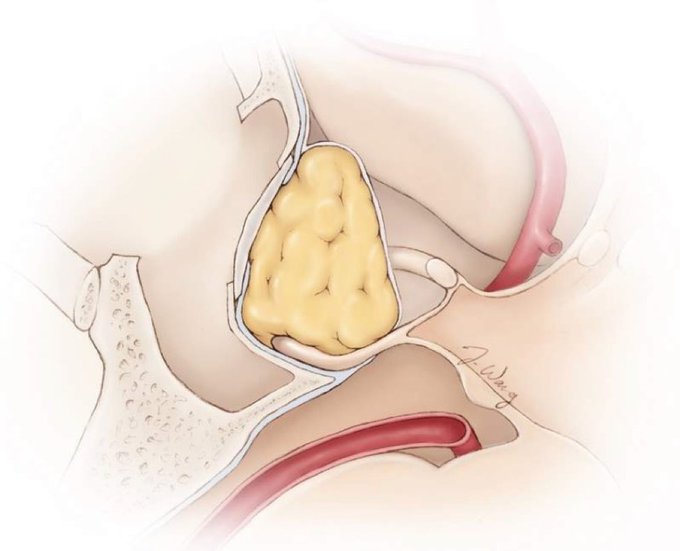
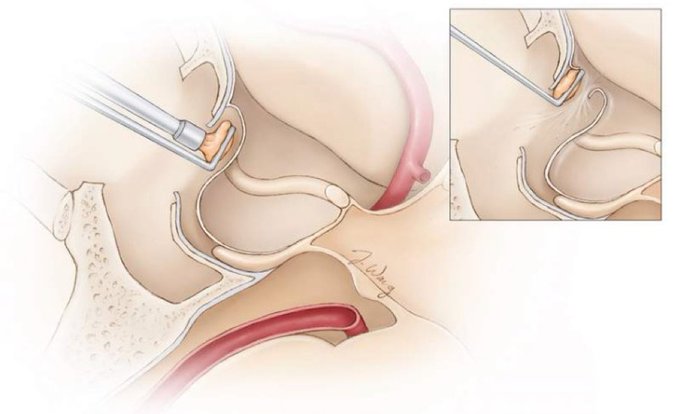
The site of diaphragm attachment to the tuberculum sella (inset) can be a “blind spot” for surgeons and can tear during tumor removal in the anterior sellar recess. Visit the link below for more on #skullbase reconstruction and CSF leak repair. #nsgy
https://t.co/n7CYeVpcaO
Exceptional illustration to aid in understanding the cerebrovascular associations within the medial temporal region.
Find this image and more on: https://t.co/1usRnkZ8m6
#nsgy #Rhoton #Neurosurgery
The black line marks the ideal size for a #decompressive #craniectomy, while the red line is too restrictive and could lead to strangulation of the herniating brain at the edges of the craniectomy, causing further infarction.
#nsgy #trauma
https://t.co/JMRapuE2LY
Following epidural #hematoma evacuation, #dural tenting sutures can help prevent delayed reaccumulation of hemorrhage from dural vessels. The sutures should be placed around and in the center of the bone flap.
#nsgy #trauma
https://t.co/l2xTG8so43
The #bicoronal incision should extend from the bilateral zygoma to include the vertex, 2 fingerbreadths posterior to the coronal suture. Which vital midline structure must be maintained throughout the operation?
#nsgy #decompressive #craniectomy
https://t.co/JMRapumrUq